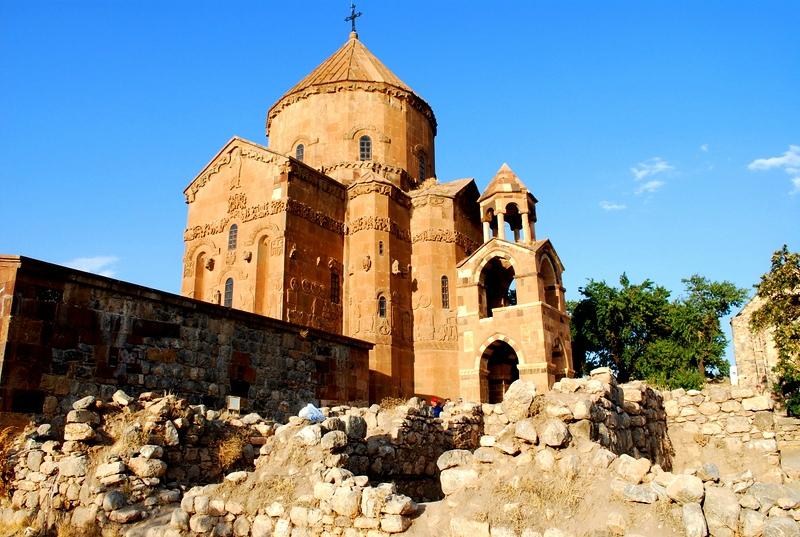
How many SURP on the Island of Van Akdamar was built in the 7th century as the Cathedral of the Holy Cross. With the order of the king Gagik I, his projects were put forward by the architect Manuel. In the southern region of the island region, it has traces of medieval Armenian art about the architecture of this church. It is also stated that these buildings are made of red Andesite stone. At the same time, rich plant and animal reliefs are located on the exterior of these buildings. It is also active for Armenian architecture. /p>
Most of the Armenian monuments in the east of the country, as a result of the collapse of the church on Akdamar Island in 1951. However, this destruction order was stopped after the efforts of Yaşar Kemal. In order to develop relations with Armenia, a political process was carried out by spending $ 1.5 million. It is known that it was opened as a museum on 29 March 2007. On September 19, 2010, Armenians of Turkey organized a ritual in the Church of Akdamar. In this ritual, the Patriarchate of the Patriarchate of the Armenians of the Turkish Patriarchate of the Patriarch General of the Patriarch, the Archbishop Aramyan ritual. For the first time after 95 years, ritual was held in this region. .PNG >
During the Van earthquake that occurred on 23 October 2011, Akdamar Church was also damaged. While the cracks were seen in the church, the windows were broken. The Church of Akdamar, which is historical for Armenians and Orthodox, is open to everyone's visit in Van. This church, which is located on the Akdamar Island in Lake Van, can be seen in general in terms of the history of Christianity. This historical area, which has a long history; It is located at a point that can be easily reached. Together with the ferry flights, reaching the Akdamar Island and starting to visit the historical areas here is called as an action that everyone can perform. In this way, detailed information about the history and religious past can be obtained. x 12.50m. The size of the four -leaf clover -shaped cross with central domed dome plan (tetraconchos). When examined in terms of exterior facades, it is seen that the cross arms in the east and west directions of the structure are kept deeper. With the addition of the jamat in 1763, this façade was closed to the height of plastic decorations. The façade is 1.10m. It is mobilized with two slits niches with width round arches. In the middle of the slit niches, there are two windows with a rectangular round arched. From these windows, it is located at the level of the ornamental border on the lower religious theme, and the top is located under the decoration border with vine winding floor. The upper part of the western cross ends with a triangular pediment. There are two rectangular windows on the north and south surfaces. The gate that provides the entrance in the jamat is 2.00m, and the width is 1.36m.
King Mahfili is located on the southern façade of the building. The outer staircase to the gallery was canceled at the end of the 18th century when the bell tower was added. The southern wall was built as five facades from the outside. 1.35m. Width 2.00m. There is a gateway to the King Mahfil just above the lower entrance. There are three window openings on top of this door and both on the side surfaces. These rectangular windows are round arched. It has a flat facade of length. This flat wall, which corresponds to both sides of the apse, 1.10m. Two vertical slits in its width are mobilized with niches. These niches are inward and round arches like those in the west. In the middle of the apse and the level of the ornament on religious themes, a rectangular -shaped window opening is located. Two smaller -sized windows are opened just below the vegetable decoration. The round arches in the south and the north is flat. The upper part of the façade is limited to a triangular pediment. Like the southern wall of the building, the northern façade, which is built with a five -facade from the outside, is closed to the level of decorating belt due to the unknown chapel which is added to the entrance door. The western surface of the northern façade can be monitored to the ground level. At the level of the main decoration belt, there is a rectangular form, round arched window. The façade is limited to a triangular pediment at the top. The cross arms located on the four facades and the central square space protrudes are covered with a double Pahli roof. The twelve -undergoned dome pulley was covered with a pyramidal cone. The eight windows opened in the pulley includes eight niches in the form of windows. The windows on the pulley have a rectangular jersey and the upper parts are round arched. The peak of the pyramidal cone is slightly destroyed. It is learned from the old narratives that there is a stone cross on the top of the conical roof1. Although the dome collapsed from the inscription on the southern façade and then repaired, but the repair was made by whom was made; Probably in the late 13th century Katholikos III. It is stated that it was repaired by Stephanos.
translates the church from a cemetery from the north and southeast. 0.85m x 1.10m of the church. thick walls on a two -digit platform. The walls of the building are knitted with red cutting tuff stones. According to a rumor, the stones used in the structure were brought from the province of Agghznikh (a region in the northeast of today's Diyarbakır). Stone material was used in the conical roof cones of the structure. This kind of application is specific to the region. The octamar church draws attention with its rich exterior reliefs that surrounds the structure of the structure at different heights. In addition, the inner part of the structure is decorated with frescoes. It is located on Akdamar Island of Gevaş district. You can visit the church every day of the week between 08:00 and 20:00. The entrances to the church are completely free. & Nbsp; You can add the historical place and the museum to your route.

 English
English Türkçe
Türkçe